Periodontal Disease
Periodontal di sease is painless and you may not be aware of it! Periodontal disease attacks your gums and the bone that support your teeth. It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums due to plaque accumulation. It is the number one reason for tooth loss. Research suggests that there may be a link between periodontal disease and other diseases such as, stroke, bacterial pneumonia, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and increased risk of premature birth.
sease is painless and you may not be aware of it! Periodontal disease attacks your gums and the bone that support your teeth. It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums due to plaque accumulation. It is the number one reason for tooth loss. Research suggests that there may be a link between periodontal disease and other diseases such as, stroke, bacterial pneumonia, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and increased risk of premature birth.
Plaque
Plaque is an invisible sticky film composed primarily of food debris, bacteria and saliva which turns into calculus (tartar). Tartar is a hard substance that cannot be removed by brushing and flossing. You will need a professional cleaning to remove it. Plaque that stays on your teeth longer than two or three days can harden into calculus which becomes a bacterial reservoir that leads to gum inflammation.
Signs and symptoms of periodontal disease:
- Bleeding gums
- Red, swollen and puffy gums
- Tender gums
- Loose teeth
- Persistent bad breath
- Pus around the teeth and gums
- Receding gums
- New space between your teeth
Stages of Periodontal Disease
It only takes twenty four hours for plaque to turn into calculus. Bacteria and calculus accumulation left untreated can cause irritation to your gums and the bone that support your teeth. Periodontal diseases range from mild gingivitis to more severe periodontitis.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the most common form of periodontal disease. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
Signs of Gingivitis:
- Swelling
- Redness
- Pain
- Bleeding of the gums
Who’s At Risk for Gingivitis?
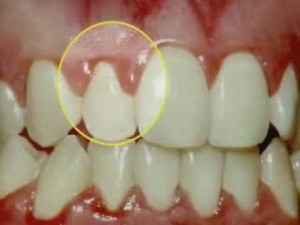 Certain people are more susceptible to gingivitis. Although plaque is by far the most common cause of gingivitis, other factors can contribute to or aggravate the condition. Stress, smoking, poor nutrition, certain medications and other underlying diseases and conditions can cause gingivitis.
Certain people are more susceptible to gingivitis. Although plaque is by far the most common cause of gingivitis, other factors can contribute to or aggravate the condition. Stress, smoking, poor nutrition, certain medications and other underlying diseases and conditions can cause gingivitis.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. Toxins from bacterial accumulation cause chronic inflammatory reaction that can destroy the bone supporting your teeth and forms periodontal pocketing. As the disease progresses, the affected teeth will become very loose and may be lost. Periodontitis can progress from mild to a more severe disease.
Risk factors for Periodontitis:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking
- Lack or infrequent professional dental care
- Diabetes
- Genetics
- Poor Nutrition
- Medications
- Immune disease
Diagnosis
Periodontal disease is diagnosed by your dentist or dental hygienist. This type of exam should always be part of your regular dental check-up.
Treatment
At Dental Wellness and Health, Dr. Chahine and her dental hygienist will evaluate your periodontal health and discuss appropriate treatment options based on the severity of your periodontal disease.
Maintenance
Once your periodontal treatment has been completed, we will help you in designing a customized maintenance program to keep your perfect smile perfect.

